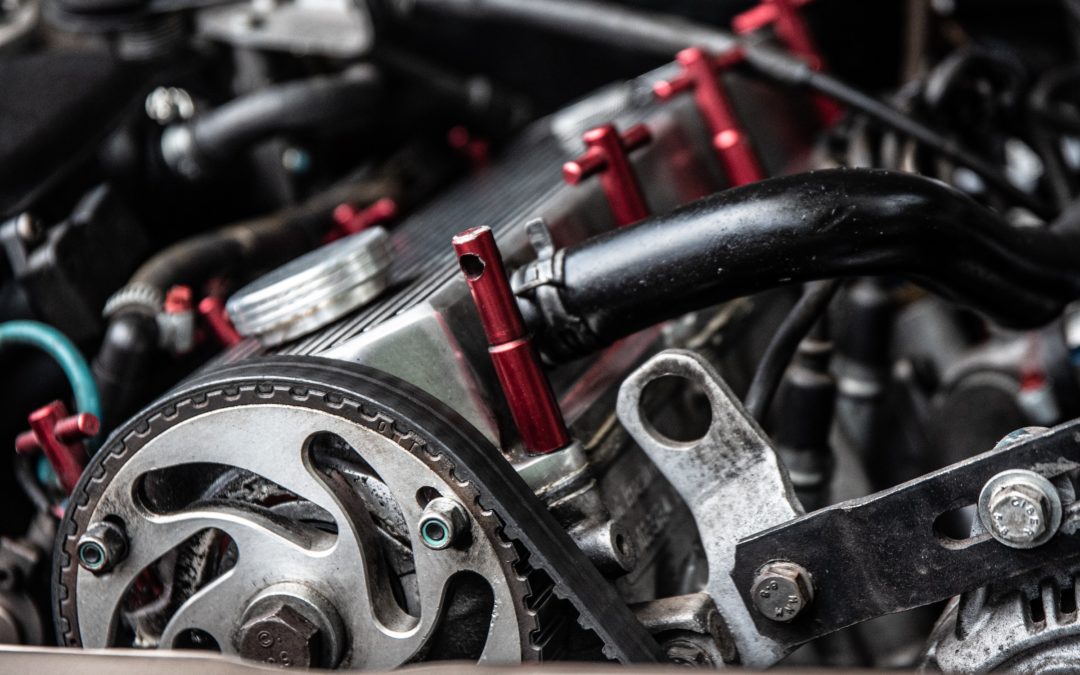
If you are diligent about your vehicle’s ongoing maintenance, then you probably have your belts inspected on a periodic basis. If not, this should be added to your maintenance routine. One common problem that you may encounter with your vehicle belts involves the “belt tensioner”. In this month’s blog, we review the importance of belts, and how the belt tensioner can be a culprit in the proper operation of your belts.
Vehicle Belts 101
Vehicle belts play a critical role in the operation of your engine and various components or accessories. Your vehicle may be equipped with one or more belt to generate power to various functions.
- Serpentine Belts: Serpentine belts are single, long, and reinforced rubber bets that are guided through the outside of the engine. If your vehicle has only one belt, then the serpentine belt may serve many purposes. For the most part, the serpentine belt weaves through the engine to provide power to engine components and accessories like your alternator, AC system, power steering, and water pump.
- Drive Belts: Your vehicle may have a separate drive belt, which is also sometimes referred to as the timing belt. Connected to the crankshaft, this belt supplies constant motion to the valves and pistons to support the internal combustion process.
There may also be cases where you have multiple engine belts, called v-belts. V-belts are found in older model vehicles and serve the same purpose as the serpentine belt. The primary difference with the v-belts is that they are not as long and may only support a single function, like powering the alternator. V-belts were used in older vehicles to make repairs easier and not impact the function of all engine components simultaneously in the event of failure.
The Belt Tensioner
The belt tensioner is an important part of the belt system, whether it is serpentine or drive belts. In simplest terms, the belt tensioner provides the right amount of tension, or resistance, to the belt so it can continue to move without any problems. When a belt is too slack, it can easily impact the ability to provide full or any power to necessary components.
The belt tensioner accomplishes its purpose through a pulley and spring system. There are manual tensioners, and automatic ones. Manual tensioners require a mechanic to adjust the tension and set it to the right level of resistance for the belt. With an automatic tensioner, the resistance is continuously controlled by springs.
Belt Tensioner Issues
The belt tensioner can become worn from the usual suspects – dirt, friction, heat, and other factors. When the tensioner begins to fail, it will impact the performance of your vehicle’s belts.
Key symptoms to consider if you think that your belt tensioner has a problem include:
- Clicking, squeaking or other unusual sounds coming from the engine. Sometimes at ignition, or when you begin to accelerate. This may be the result of a loose or slack belt making noises because it is not operating at the right resistance.
- Failure of vehicle components such as the water pump or AC. If you suddenly have those systems fail, especially simultaneously, this may indicate a problem with the tensioner that has impacted the belt performance.
- The actual belts may sometimes show excessive wear or fraying on the edges if there are tensioner issues.
- If you experience any of these problems, it’s advisable to have your vehicle inspected as soon as possible. While tensioner issues do not hinder your ability to drive, they may lead to further complications with important components of your vehicle. Tensioner issues can end up being a bigger problem if neglected, including damage to other accessories, or failure to operate the vehicle due to a belt break or inability to power the pistons and valves.
Don’t ignore your belts. Contact the service professionals at Campus Repair today to schedule an appointment to have your belts and tensioner inspected and/or repaired.